Last universal common ancestor (LUCA): Difference between revisions
(Created page) |
(Added diagram) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Last universal common ancestor | The '''Last universal common ancestor''', known as '''LUCA''' is the most recent population from which all organisms now living on Earth share common descent, i.e., the most recent common ancestor of all current life on Earth. | ||
[[File:Phylogenetic_tree_of_life_1990_LUCA.png|400px]] | |||
According to Wikipedia, even though there is no specific fossil evidence of the LUCA, the detailed biochemical similarity of all current life confirms its existence. Its characteristics can be inferred from shared features of modern genomes. These genes describe a complex life form with many co-adapted features, including [[Transcription|transcription]] and [[Translation|translation]] mechanisms to convert information from DNA to RNA to proteins. | |||
The LUCA probably lived in the high-temperature water of deep-sea vents near ocean-floor magma flows around 4 billion years ago. | |||
[[Category: G-Definitions]] | [[Category: G-Definitions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:01, 28 January 2023
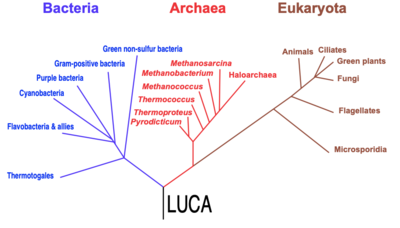
The Last universal common ancestor, known as LUCA is the most recent population from which all organisms now living on Earth share common descent, i.e., the most recent common ancestor of all current life on Earth.
According to Wikipedia, even though there is no specific fossil evidence of the LUCA, the detailed biochemical similarity of all current life confirms its existence. Its characteristics can be inferred from shared features of modern genomes. These genes describe a complex life form with many co-adapted features, including transcription and translation mechanisms to convert information from DNA to RNA to proteins.
The LUCA probably lived in the high-temperature water of deep-sea vents near ocean-floor magma flows around 4 billion years ago.